Most law firms are deeply in (or about to enter) budget season. We surveyed law firm leaders last year regarding best practices around budget development. As a seasonal follow-up to that survey, we offer the following five tips to improve the alignment of law firm strategy with annual budgets.
Engage Practice Group Leaders Directly in the Budget Development Process
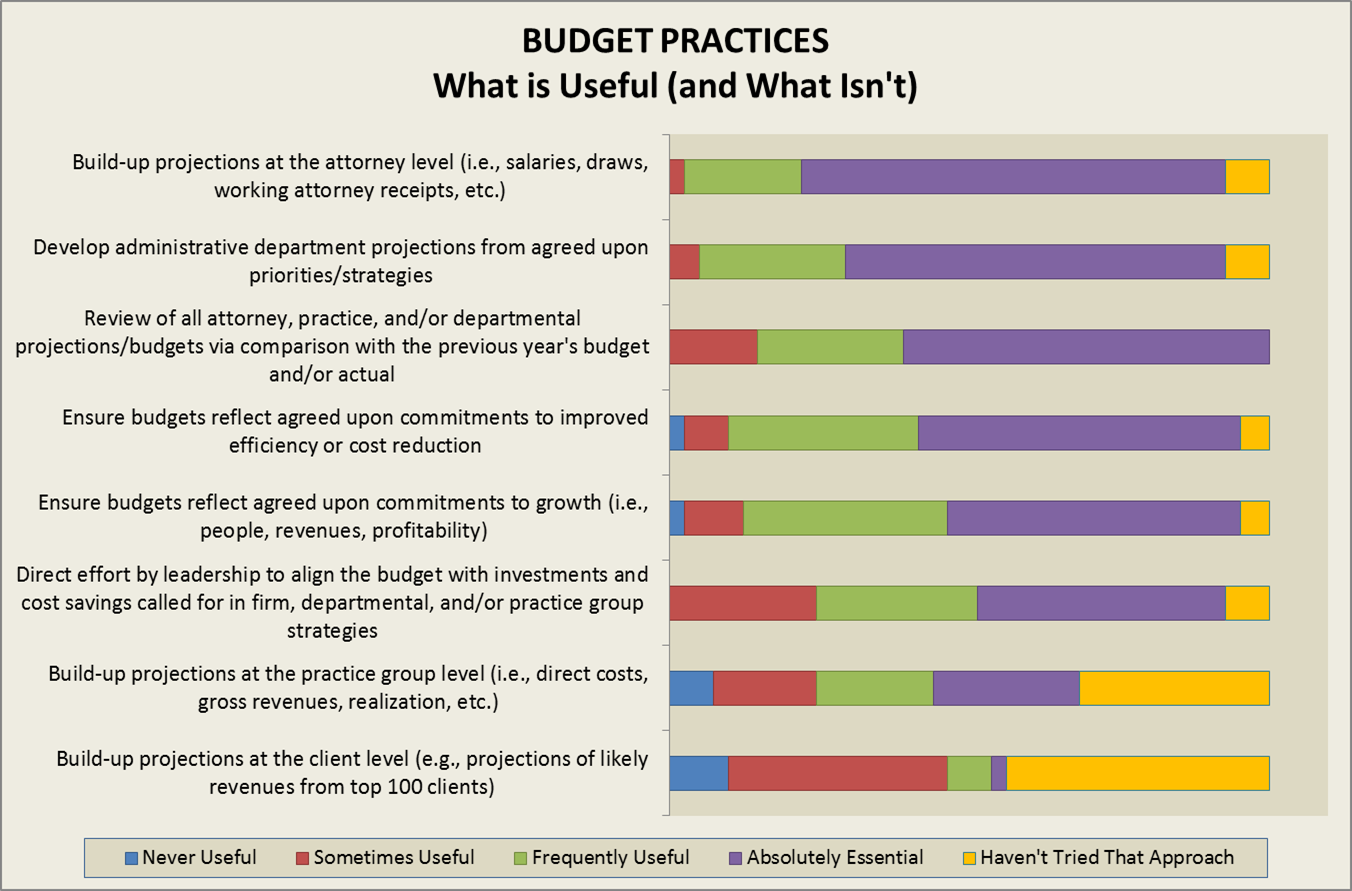
A surprisingly high percentage (44%) of firms in last year’s survey reported that they do not build budget projects from the practice groups up (i.e., direct costs, gross revenues, realizations, etc.). The budget development process provides an excellent opportunity to cascade firm strategy (and strategy implementation) to the practice group level.
Engaging practice group leaders in budgeting – in thinking about cost drivers, revenue drivers and factors that contribute to client satisfaction (which often translates to realizations) – helps to “connect the dots” for people. It highlights how strategies are being operationalized in the practices and makes those connections tangible in financial terms.
Budget for R&D
What does the average partner (i.e., the partner not involved in management) think about budgets? Mainly, he/she wants the firm to beat its budget so that distributable income is higher than projected – creating a pool of funds that can pay partners more than their “expected compensation.”
By explicitly budgeting for R&D (both time investments and direct costs), the tension between partners’ desire to distribute all income at year end and the firm’s need to invest for the long term is mitigated. Essentially, R&D projects should be prioritized along with other investments (see the next section). At year end, assuming the firm had a good year, everyone is happy. The firm has made needed investments for its future. The partners get distributions above what was budgeted.
Prioritize Budgets in Financial and Strategic Terms
Law firm leaders (especially COOs and CFOs) are very comfortable thinking about projects and initiatives in financial terms. Projects with high returns on investment (ROI) and/or fast payback are a higher priority than low return projects – a blinding glimpse of the obvious (a la Barbarians at the Gate).
In addition to the financial perspective, we recommend adding consideration of the expected strategic impact of a project to the prioritization process. Essentially, projects that contribute to multiple strategic goals (i.e., that are more “mission critical”) are higher priority initiatives. For example, a Knowledge Management project may contribute to achieving goals associated with client satisfaction; improved efficiency/value; and improved predictability. Contrast that with a project to reconfigure office space – which may have a high ROI, but relatively little strategic impact.
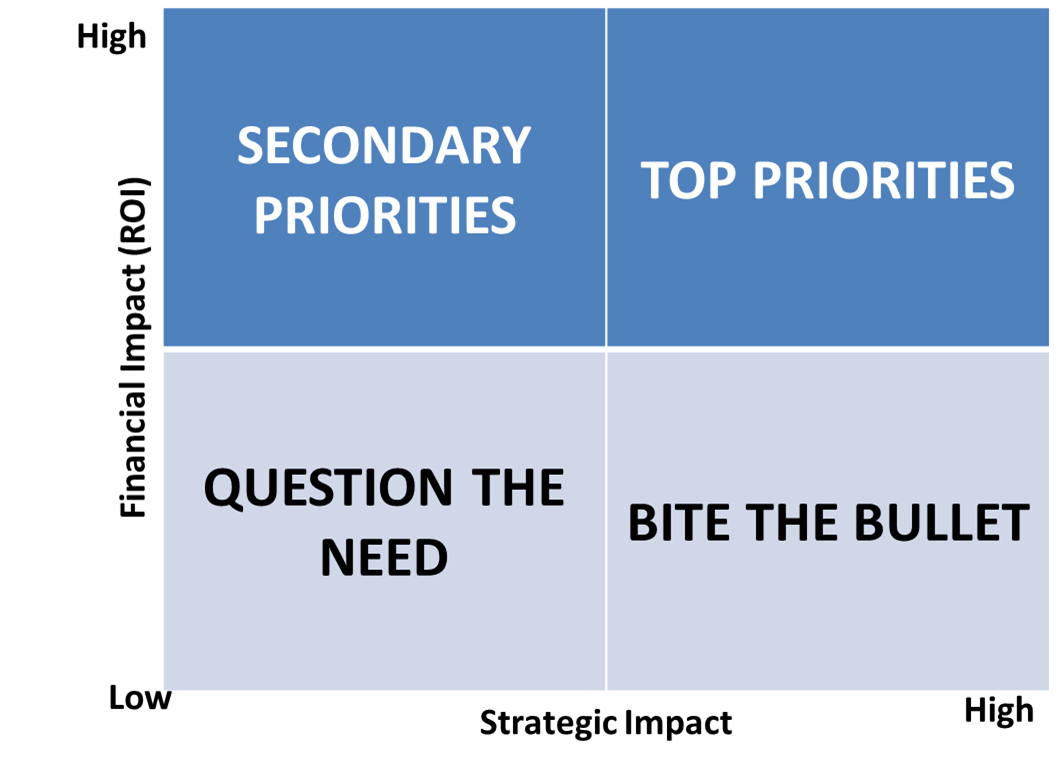
Prioritization across both dimensions (financial and strategic) yields added clarity on what the priorities really need to be across a range of projects – and may even lead a firm to delay or spike selected projects.
Validate Revenue Projections by Taking a Client (bottom-up) View
Revenue projects are (more often than not) built on the basis of headcount, anticipated hours, and rates (i.e., FTE x Hours x Realized Rates = Gross Revenues). That is entirely logical and appropriate. However, a nice check on that approach is to look at revenues from a client perspective.
At many firms, the top 50 clients (plus or minus) represent a substantial share of total revenues (often well over 50%). By asking relationship partners what those major clients are expected to do in the coming year, a firm can help to validate its revenue projections. If most of the major clients are expected to continue to generate similar or higher revenue streams, great. However, if revenues from important clients are expected to fall (e.g., a major case has been resolved, the company has been sold, etc.), it may lead the firm to make important adjustments to its budget.
Align with Other Metrics – Financial and Non-Financial
Last December we asked law firm leaders where they had reliable metrics and where they did not. Over 95% of firms have solid, reliable financial metrics. Metrics associated with client satisfaction, people development, and business processes are more spotty – though those kinds of metrics do exist on at least a limited basis.
The budget process provides an opportunityfor firm and practice group leaders to think about and revisit financial and non-financial metrics. Essentially, it is an opportunity to ask the question, “If we make or exceed this budget, will we also achieve our other measurable objectives?” Similarly, it is an opportunity to ask, “Are the financial and non-financial metrics we have adopted to track the success (or lack thereof) of our strategy consistent with the budget we are about to propose and approve?”
Essentially, the budget process becomes another tool to help a firm and its practice groups effectively use a balanced scorecard to monitor and drive strategy implementation.
* * * *
As always we welcome your comments and insights – in the comment section below, via email at info@sterlingstrat.com, and over the phone at (312) 543-6616.