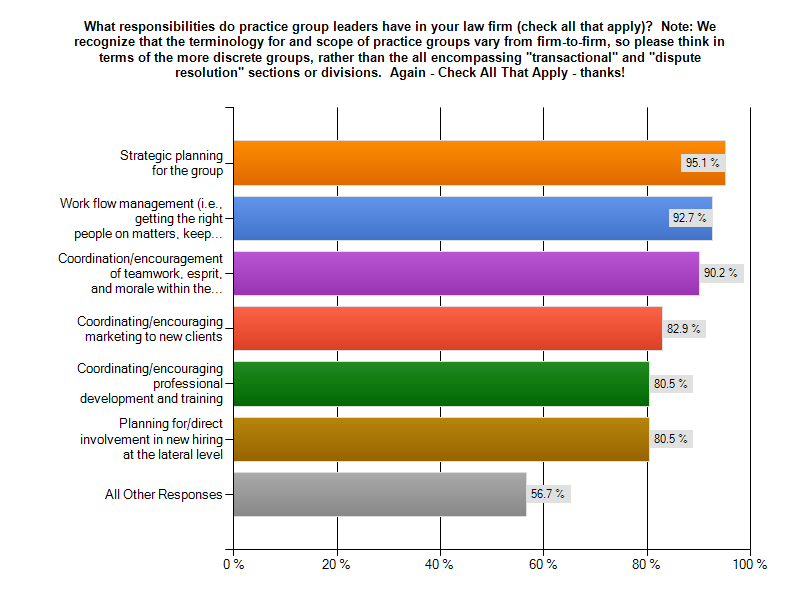
Having great attorneys – well-trained, highly capable, hard-working and client focused – has long been a critical success factor for law firms. Strategically, it has become basic table stakes for competing effectively in the legal industry, particularly among more sophisticated law firms (i.e., BigLaw and BigEnoughLaw). The big change coming to the legal industry is the growing criticality of non-lawyers. Yet, it is currently an area in which many otherwise sophisticated law firms fail miserably.
Think about it for a moment. Where else (besides large and mid-sized law firms) do highly educated professionals get placed on such limited career paths, essentially for lack of a JD? Furthermore, what is it about obtaining a JD that qualifies a person as an expert in information technology, project management, business development, process redesign, innovation, knowledge management or really anything besides the law and precedent? As Bruce MacEwen astutely observed in his Growth is Dead e-book, “lawyers are inclined to assume they can do anyone else’s job but no one else could possibly do what they do.”
The very term “non-lawyers” is a peculiar construct of law firms. And, at many firms it is used in a way that devalues, even marginalizes, professionals who are not lawyers by training and education. Given the trends affecting the legal industry, especially the trends facing sophisticated law firms, those with a cultural predisposition that devalues so-called non-lawyers will be at a distinct disadvantage in the future. Consider three examples where non-lawyers will be critical to success.
Responding to Macro-Level Trends
The most obvious arena in which non-lawyers will drive the success or failure of law firms is in response to the macro-level trends influencing the more sophisticated segments of the legal industry. Richard Susskind’s book is called The End of Lawyers in large part because it foretells a future in which legal training and expertise are necessary, but insufficient for survival and prosperity. More sophisticated law firms will be (are being) forced by clients and competitors to embrace technology, knowledge management, project management, lean process, and other management tools more common outside the legal industry.
Successfully adopting any of those management tools requires attracting great people – well-trained, highly capable, hard-working and client focused – whose professional training is grounded in engineering, information technology, organizational psychology, management, and other fields. Their training and backgrounds will not include a JD or a background practicing law (with rare exceptions). Even in cases where those functional managers do have a JD, it will not be instrumental to the contribution they make to the success of their law firm.
In short, winning law firms in the future will attract (and will highly value) professionals across a range of professional disciplines. Attorneys will defer to the expertise these professionals bring to the table. And, attorneys will collaborate effectively with those professionals to apply their expertise to the firm’s practice and its relationships with clients.
Business Development and Marketing
Over the past twenty years, marketing professionals have been gradually gaining credibility and respect in law firms. Marketing and business development positions have been elevated within the management hierarchy and investment in the leadership positions appears to be rising. However, there is a long way to go to fully capitalize on the expertise of marketing and business development professionals in law firms.
As long as powerful partners can push marketing and business development professionals (and their own partners) away from direct contact with select clients, the firm is at a disadvantage and at risk. That risk includes the potential of losing the partner (and his/her clients) to a lateral move. Frankly, partners who keep others away from “their clients” raise a number of red flags. Beyond the risk of purely mercenary behavior on the part of a partner, a lack of broader contact risks the loss of the client relationship. Studies demonstrate that clients with multiple partner relationships and/or that use multiple practice groups are much more likely to remain with a firm. Further, that broader contact improves the probability that emerging and/or nagging problems (e.g., responsiveness, pricing, quality of work, etc.) will surface before a client shops their work to other law firms.
Looking forward, business development and marketing professionals will play an increasingly important role in a number of areas including: gathering genuine, actionable client feedback; expanding existing client relationships (e.g., facilitating cross-marketing); identifying opportunities to deepen and strengthen existing relationships via process improvement, technology, pricing and other innovations. Marginalize marketing and business development professionals at your own risk.
Delivering Cost Effective Legal Services
Perhaps the most challenging (or controversial) change coming to the legal industry is the inevitability of involving more non-lawyers in the direct delivery of client services. That growing involvement of non-lawyers will go well beyond (though it will include) the use of paralegals over the next five to ten years.
Ask yourself a few questions (thought experiments if you will). Who is a better value to clients in managing document discovery, a well-trained paraprofessional with expertise in IT, database searches and document management or an associate earning three to four times the salary (with less grounding in large scale document management)? Can a $60,000 per year professional with a finance degree add value to a transactions team (perhaps many times more value than a junior associate)? Can a trained actuary add value to risk management assessments for major litigation clients?
Certainly, some firms have already made great strides in the use of non-attorneys in the delivery of legal services. For instance, the best IP practices and firms are loaded with PhD and Masters level technical specialists. In the future, firms across the practice spectrum will be challenged to become much more creative in integrating non-attorney professionals into their client service teams. That will be especially evident in practices where clients and/or competition drive the market toward more cost effective solutions.
* * * *
So, if your firm still has a culture that devalues non-lawyers – that doesn’t draw upon the knowledge and expertise of other professionals – you better get started on changing that culture. No silver bullet (technology or otherwise) will save you in the long run if the only voices that matter in your law firm are attorney voices (or even more narrowly, partner voices).